Consider Again the Problem of Merging K Sorted Length-n Arrays
Giving k sorted arrays, each of size Northward, the chore is to merge them into a single sorted assortment.
Examples:
Input: arr[][] = {{5, vii, xv, 18}, {one, 8, 9, 17}, {1, 4, 7, vii}} Output: {ane, ane, iv, 5, seven, vii, 7, 8, 9, 15, 17, 18} Input: arr[][] = {{3, 2, 1} {6, 5, 4}} Output: {1, 2, three, 4, 5, half-dozen} Prerequisite: Merge Sort
Simple Arroyo: A simple solution is to append all the arrays one after some other and sort them.
C++fourteen
#include <$.25/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define North iv
void merge_and_sort(
vector< int > &output, vector<vector< int >> arr,
int due north, int m)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < thousand; i++) {
for ( int j = 0; j < northward; j++) {
output[(i * n) + j] = arr[i][j];
}
}
sort(output.begin(), output.terminate());
}
int main()
{
vector<vector< int >> arr = { { 5, 7, xv, 18 },
{ 1, 8, 9, 17 },
{ 1, 4, seven, 7 } };
int n = N;
int k = arr.size();
vector< int > output(n*g);
merge_and_sort(output, arr, n, k);
for ( int i = 0; i < north * k; i++)
cout << output[i] << " " ;
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int N = iv ;
static void merge_and_sort( int output[], int arr[][],
int n, int yard)
{
for ( int i = 0 ; i < k; i++)
{
for ( int j = 0 ; j < n; j++)
{
output[i * n + j] = arr[i][j];
}
}
Arrays.sort(output);
}
public static void primary(String[] args)
{
int arr[][] = { { 5 , 7 , 15 , 18 },
{ ane , eight , 9 , 17 },
{ 1 , 4 , 7 , vii } };
int north = Due north;
int grand = arr.length;
int output[] = new int [n * k];
merge_and_sort(output, arr, n, thou);
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n * k; i++)
System.out.print(output[i] + " " );
}
}
Python3
Due north = 4
def merge_and_sort(output, arr, n, k):
for i in range (k):
for j in range (n):
output[i * n + j] = arr[i][j];
output.sort()
if __name__ = = '__main__' :
arr = [ [ 5 , 7 , 15 , 18 ],
[ ane , 8 , ix , 17 ],
[ i , 4 , vii , seven ] ];
northward = N;
k = len (arr)
output = [ 0 for i in range (n * 1000)]
merge_and_sort(output, arr, n, one thousand);
for i in range (northward * one thousand):
print (output[i], stop = ' ' )
C#
using System;
grade GFG
{
static int N = iv;
static void merge_and_sort( int [] output, int [,] arr,
int n, int g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
for ( int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
output[i * n + j] = arr[i,j];
}
}
Array.Sort(output);
}
static void Main()
{
int [,] arr = { { five, vii, 15, 18 },
{ one, 8, 9, 17 },
{ 1, four, 7, seven } };
int due north = N;
int k = arr.GetLength(0);
int [] output = new int [northward * k];
merge_and_sort(output, arr, n, yard);
for ( int i = 0; i < northward * one thousand; i++)
Panel.Write(output[i] + " " );
}
}
Javascript
<script>
allow Northward = 4;
function merge_and_sort(output, arr, northward, k)
{
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
for (permit j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
output[i * north + j] = arr[i][j];
}
}
output.sort( function (a, b){ render a - b});
}
let arr = [ [ v, seven, 15, 18 ],
[ 1, eight, nine, 17 ],
[ 1, iv, vii, seven ] ];
let n = N;
let k = 3;
let output = new Array(northward * k);
merge_and_sort(output, arr, n, k);
for (let i = 0; i < n * k; i++)
document.write(output[i] + " " );
</script>
Output:
ane 1 4 v 7 vii 7 8 9 fifteen 17 xviii
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(Due north*g*log(N*k)).
The size of all elements is n*yard and then the time complexity is O(N*k * log(N*k)) - Space Complexity: O(N*chiliad).
To store the output assortment O(N*k) space is required.
Efficient Solution :
Approach: The idea becomes clear once we starting time looking at the 1000 arrays as the intermediate state of the merge sort algorithm.
Since there are k arrays that are already sorted, merge the m arrays. Create a recursive function which will take k arrays and divide them into 2 parts and call the function recursively with each half. The base cases are when the value of k is less than 3.
Encounter this article to merge two arrays in O(n) fourth dimension.
Algorithm:
- Initialize the output array with the size N*k.
- Call the function divide. Let
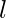 and
and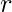 represent the range of arrays that are to be merged and thus vary betwixt 0 to k-1.
represent the range of arrays that are to be merged and thus vary betwixt 0 to k-1. - At each step, we call the left and correct half of the range recursively so that, they will be sorted and stored in the output array.
- After that, we merge the left and right one-half. For merging, we demand to make up one's mind the range of indexes for the left and right halves in the output assortment. We can easily observe that.
- Left function will first from the alphabetize l * n of the output assortment.
- Similarly, right part volition get-go from the index ((l + r) / two + 1) * north of the output array.
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#ascertain northward four
using namespace std;
void merge( int l, int r, vector< int >& output)
{
int l_in = l * n, r_in
= ((l + r) / 2 + 1) * n;
int l_c = ((l + r) / ii - l + 1) * n;
int r_c = (r - (fifty + r) / 2) * n;
int l_arr[l_c], r_arr[r_c];
for ( int i = 0; i < l_c; i++)
l_arr[i] = output[l_in + i];
for ( int i = 0; i < r_c; i++)
r_arr[i] = output[r_in + i];
int l_curr = 0, r_curr = 0;
int in = l_in;
while (
l_curr + r_curr < l_c + r_c) {
if (
r_curr == r_c
|| (l_curr != l_c
&& l_arr[l_curr] < r_arr[r_curr]))
output[in]
= l_arr[l_curr],
l_curr++, in++;
else
output[in]
= r_arr[r_curr],
r_curr++, in++;
}
}
void divide( int fifty, int r, vector< int >& output,
vector<vector< int >> arr)
{
if (fifty == r) {
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++)
output[l * northward + i] = arr[50][i];
return ;
}
split(l, (l + r) / 2,
output, arr);
divide((l + r) / ii + i, r,
output, arr);
merge(l, r, output);
}
int main()
{
vector<vector< int >> arr = { { v, 7, xv, 18 },
{ i, viii, 9, 17 },
{ 1, 4, 7, vii } };
int k = arr.size();
vector< int > output(n*k);
divide(0, k - 1, output, arr);
for ( int i = 0; i < north * k; i++)
cout << output[i] << " " ;
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
course GFG {
static int n = iv ;
static void merge(
int 50, int r, int [] output)
{
int l_in = l * n, r_in
= ((fifty + r) / two + 1 ) * n;
int l_c = ((l + r) / two - fifty + ane ) * due north;
int r_c = (r - (l + r) / 2 ) * n;
int l_arr[] = new int [l_c],
r_arr[] = new int [r_c];
for ( int i = 0 ; i < l_c; i++)
l_arr[i] = output[l_in + i];
for ( int i = 0 ; i < r_c; i++)
r_arr[i] = output[r_in + i];
int l_curr = 0 , r_curr = 0 ;
int in = l_in;
while (l_curr + r_curr < l_c + r_c) {
if (
r_curr == r_c
|| (l_curr != l_c
&& l_arr[l_curr] < r_arr[r_curr])) {
output[in] = l_arr[l_curr];
l_curr++;
in++;
}
else {
output[in] = r_arr[r_curr];
r_curr++;
in++;
}
}
}
static void split( int l, int r, int [] output,
int arr[][])
{
if (l == r) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < due north; i++)
output[l * n + i] = arr[l][i];
return ;
}
separate(fifty, (l + r) / 2 , output, arr);
split up((l + r) / 2 + i , r, output, arr);
merge(fifty, r, output);
}
public static void main(Cord[] args)
{
int arr[][] = { { v , seven , fifteen , eighteen },
{ 1 , viii , ix , 17 },
{ 1 , four , seven , 7 } };
int yard = arr.length;
int [] output = new int [n * k];
separate( 0 , chiliad - one , output, arr);
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n * k; i++)
Arrangement.out.print(output[i] + " " );
}
}
Python3
north = 4 ;
def merge(l, r, output) :
l_in = l * n ;
r_in = ((l + r) / / ii + 1 ) * n;
l_c = ((l + r) / / 2 - l + one ) * northward;
r_c = (r - (l + r) / / two ) * northward;
l_arr = [ 0 ] * l_c; r_arr = [ 0 ] * r_c;
for i in range (l_c) :
l_arr[i] = output[l_in + i];
for i in range (r_c) :
r_arr[i] = output[r_in + i];
l_curr = 0 ; r_curr = 0 ;
in1 = l_in;
while (l_curr + r_curr < l_c + r_c) :
if (r_curr = = r_c or (l_curr ! = l_c and
l_arr[l_curr] < r_arr[r_curr])) :
output[in1] = l_arr[l_curr];
l_curr + = 1 ; in1 + = i ;
else :
output[in1] = r_arr[r_curr];
r_curr + = 1 ; in1 + = 1 ;
def carve up(l, r, output, arr) :
if (l = = r) :
for i in range (n) :
output[l * n + i] = arr[l][i];
return ;
split up(50, (l + r) / / 2 , output, arr);
dissever((50 + r) / / ii + 1 , r, output, arr);
merge(fifty, r, output);
if __name__ = = "__main__" :
arr = [[ 5 , 7 , 15 , xviii ],
[ 1 , 8 , 9 , 17 ],
[ 1 , iv , 7 , seven ]];
g = len (arr);
output = [ 0 ] * (northward * chiliad);
divide( 0 , thou - 1 , output, arr);
for i in range (northward * g) :
print (output[i], end = " " );
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int n = 4;
static void merge( int fifty, int r, int [] output)
{
int l_in = l * n, r_in = ((50 + r) / 2 + 1) * n;
int l_c = ((l + r) / two - l + ane) * n;
int r_c = (r - (l + r) / 2) * n;
int [] l_arr = new int [l_c];
int [] r_arr = new int [r_c];
for ( int i = 0; i < l_c; i++)
l_arr[i] = output[l_in + i];
for ( int i = 0; i < r_c; i++)
r_arr[i] = output[r_in + i];
int l_curr = 0, r_curr = 0;
int index = l_in;
while (l_curr + r_curr < l_c + r_c) {
if (r_curr == r_c || (l_curr != l_c && l_arr[l_curr] < r_arr[r_curr])) {
output[alphabetize] = l_arr[l_curr];
l_curr++;
alphabetize++;
}
else {
output[index] = r_arr[r_curr];
r_curr++;
alphabetize++;
}
}
}
static void separate( int l, int r, int [] output,
int [, ] arr)
{
if (l == r) {
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++)
output[l * n + i] = arr[l, i];
return ;
}
split(l, (50 + r) / ii, output, arr);
split up((l + r) / 2 + i, r, output, arr);
merge(l, r, output);
}
public static void Master(Cord[] args)
{
int [, ] arr = { { 5, 7, xv, 18 },
{ 1, 8, 9, 17 },
{ 1, 4, 7, 7 } };
int k = arr.GetLength(0);
int [] output = new int [n * k];
separate(0, one thousand - 1, output, arr);
for ( int i = 0; i < n * k; i++)
Console.Write(output[i] + " " );
}
}
PHP
<?php
$n = 4;
function merge( $l , $r , & $output )
{
global $northward ;
$l_in = $l * $northward ;
$r_in = ((int)(( $50 + $r ) / 2) + one) * $northward ;
$l_c = (int)(((( $fifty + $r ) / 2) - $l + 1) * $n );
$r_c = ( $r - (int)(( $50 + $r ) / 2)) * $n ;
$l_arr = array_fill (0, $l_c , 0);
$r_arr = array_fill (0, $r_c , 0);
for ( $i = 0; $i < $l_c ; $i ++)
$l_arr [ $i ] = $output [ $l_in + $i ];
for ( $i = 0; $i < $r_c ; $i ++)
$r_arr [ $i ] = $output [ $r_in + $i ];
$l_curr = 0;
$r_curr = 0;
$in = $l_in ;
while ( $l_curr + $r_curr < $l_c + $r_c )
{
if ( $r_curr == $r_c || ( $l_curr != $l_c &&
$l_arr [ $l_curr ] < $r_arr [ $r_curr ]))
{
$output [ $in ] = $l_arr [ $l_curr ];
$l_curr ++; $in ++;
}
else
{
$output [ $in ] = $r_arr [ $r_curr ];
$r_curr ++; $in ++;
}
}
}
role divide( $50 , $r , & $output , $arr )
{
global $n ;
if ( $l == $r )
{
for ( $i = 0; $i < $n ; $i ++)
$output [ $50 * $n + $i ] = $arr [ $l ][ $i ];
return ;
}
divide( $50 , (int)(( $l + $r ) / 2), $output , $arr );
split up((int)(( $l + $r ) / ii) + 1, $r , $output , $arr );
merge( $l , $r , $output );
}
$arr = array ( array ( 5, 7, 15, 18 ),
array ( one, 8, 9, 17 ),
assortment ( 1, 4, 7, 7 ));
$k = count ( $arr );
$output = array_fill (0, $n * $k , 0);
divide(0, $1000 - 1, $output , $arr );
for ( $i = 0; $i < $n * $k ; $i ++)
print ( $output [ $i ] . " " );
?>
Javascript
<script>
var n = 4;
function merge(l, r, output)
{
var l_in = l * n,
r_in = (parseInt((l + r) / 2) + one) * northward;
var l_c = (parseInt((l + r) / 2) - l + i) * northward;
var r_c = (r - parseInt((l + r) / 2)) * north;
var l_arr = Assortment(l_c), r_arr = Assortment(r_c);
for ( var i = 0; i < l_c; i++)
l_arr[i] = output[l_in + i];
for ( var i = 0; i < r_c; i++)
r_arr[i] = output[r_in + i];
var l_curr = 0, r_curr = 0;
var par = l_in;
while (l_curr + r_curr < l_c + r_c)
{
if (r_curr == r_c ||
(l_curr != l_c &&
l_arr[l_curr] < r_arr[r_curr]))
{
output[par] = l_arr[l_curr];
l_curr++, par++;
}
else
{
output[par] = r_arr[r_curr];
r_curr++, par++;
}
}
}
role divide(l, r, output, arr)
{
if (l == r)
{
for ( var i = 0; i < n; i++)
output[l * n + i] = arr[l][i];
return ;
}
divide(l, parseInt((l + r) / ii),
output, arr);
divide(parseInt((l + r) / two) + 1, r,
output, arr);
merge(l, r, output);
}
var arr = [ [ five, 7, 15, 18 ],
[ 1, viii, 9, 17 ],
[ one, 4, 7, 7 ] ];
var g = arr.length;
var output = Assortment(n * k);
divide(0, k - ane, output, arr);
for ( var i = 0; i < northward * grand; i++)
certificate.write(output[i] + " " );
</script>
Output:
ane 1 4 5 7 seven 7 8 9 xv 17 18
Complexity Assay:
- Time Complication: O(Due north*k*log(m)).
In each level the assortment of size N*1000 is traversed once, and the number of levels are log(grand). - Space Complexity: O(N*1000).
To shop the output array O(N*g) space is required.
We tin can also solve this problem by using min-heap.
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/merge-k-sorted-arrays-set-3-using-divide-and-conquer-approach/
0 Response to "Consider Again the Problem of Merging K Sorted Length-n Arrays"
Post a Comment